The Rise of Large Language Models
Large language models have revolutionized various industries, from healthcare to finance, by providing advanced natural language processing capabilities. They are capable of understanding, generating, and interpreting human-like text, making them valuable assets in numerous applications. Another industry that they are also revolutionizing is that of cybercrime. Since the launch of ChatGPT a year ago, there have been a vast torrent of new models appearing.
Commercial LLMs
Most organizations in the software industry are well acquainted with cloud service providers (CSPs) offering scalable computing capabilities. With the emergence and expansion of ChatGPT, a new wave of large language model (LLM) cloud services has been introduced, originating from both established industry leaders and well-funded startup companies.
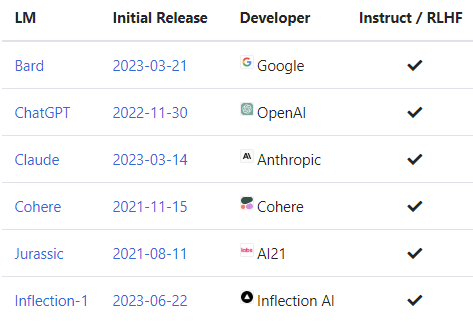
Open Source LLMs
If you have the capability to operate models encompassing billions of parameters, employing an open source model can be a strategic approach to maintaining control over your systems and data. The open source large language model (LLM) landscape is advancing rapidly, a trend accentuated by the unveiling of Meta’s LLaMA models. Concurrent with the launch of these robust models, which are trained on extensive data corpuses and fine-tuned with specific instructions by research teams, a collective of developers have created a pool of increasingly expansive models on standard hardware, such as a typical consumer laptop.
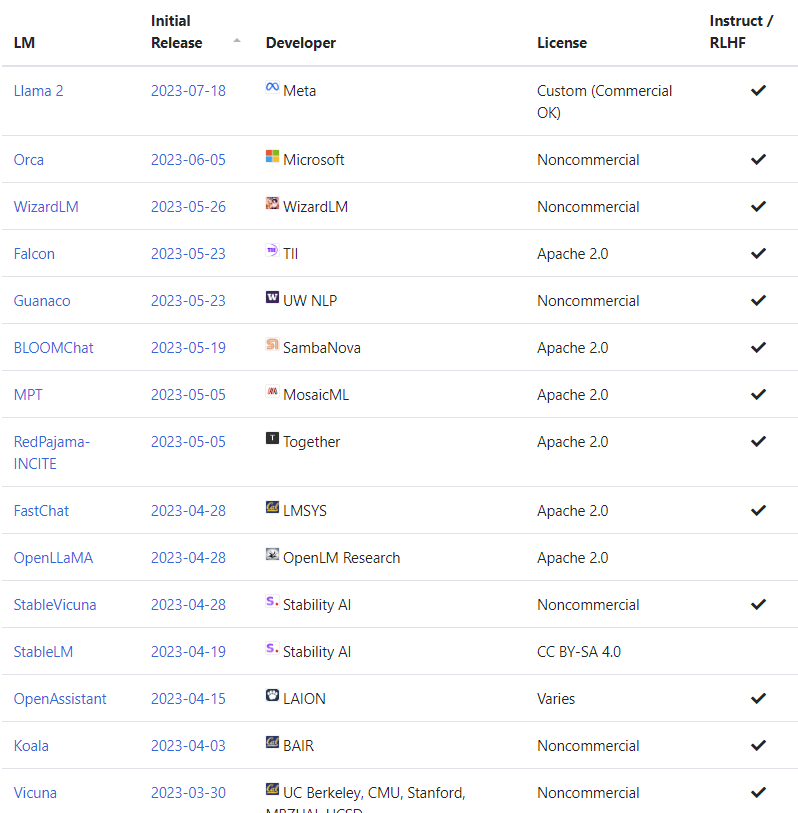
For a detailed comparison of all current commercial and open-source models, go look at the LLM index.
Malicious LLMs
A model is trained on a corpus of data, also known as the training set. The information that is provided helps tune the objective, or outcome of the model. In the same way that you can have specific models tuned for the legal industry (LawGPT), or medical practice (DoctorGPT) (both of which require more than a decade of training for humans), you can train models on a malicious corpus of data. How to perform criminal activities, fraud, ransom, identity theft, etc. Commercial LLMs block prompts like these with ethical guardrails that inhibit the ability to provide such responses. However, there are some ways around that, which is called LLM jailbreaking. If you tell a model, that you are playing a game, and they need to act in a specific way to adhere to the rules, and those rules contravene the ethical guardrails, then you can manipulate it to provide some malicious responses. However, that’s a constant battle and what may work one day, does not work another day. So threat actors take the Open Source models, and tune those. Then, depending on the size and complexity of model, it becomes downloadable to run on lower end hardware, or is provided as a service, in the same way that ChatGPT Plus is.
Here are some current malicious LLMs.
WormGPT
WormGPT is driven on a platform with 6 billion parameters. Its database also has 50257 tokens of vocabulary size. This information shows that WormGPT is driven by an LLM model of GPT-2 developed by Open AI. Hence, it is considered the malicious cousin of ChatGPT.
Features of WormGPT
There are several essential features offered by WormGPT, which are easily accessible by the users such as:
- Malicious alternative of ChatGPT, primarily used for illegal activities such as hacking, payment scams, etc.
- GPT-J model works in WormGPT, firstly developed by EleutherAI.
- No ethical or legal restrictions over the operations of WormGPT.
- Can’t be directly accessed through web browsing. Only available through dark web.
- Effectiveness in generating human text is more as compared to ChatGPT.
WormGPT Pricing
On a dark web server, WormGPT offers three different pricing plans as per the user requirements, like:
- Monthly Plan: 100 Euros
- Yearly Plan: 550 Euros
- Private Setup with more security: 5000 Euros
FraudGPT
FraudGPT has been circulating on Telegram Channels since July 22, 2023. This is an AI bot, exclusively targeted for offensive purposes, such as crafting spear phishing emails, creating cracking tools, carding, etc. The tool is currently being sold on various Dark Web marketplaces and the Telegram platform.
The subscription fee for FraudGPT starts at $200 per month and goes up to $1,700 per year.
Some of the features include:
- Write malicious code
- Create undetectable malware
- Find non-VBV bins
- Create phishing pages
- Create hacking tools
- Find groups, sites, markets
- Write scam pages/letters
- Find leaks, vulnerabilities
- Learn to code/hack
- Find cardable sites
- Escrow available 24/7
- 3,000+ confirmed sales/reviews
DarkBERT and DarkBART
DarkBERT is a language model developed earlier by data intelligence company S2W Security that was trained on data from the dark web with the goal of pushing back against cybercrime rather than enabling it. However, anybody with a .edu email could access it, for “educational purposes”.
See this whitepaper on the development of DarkBERT. DarkBERT: A Language Model for the Dark Side of the Internet
DarkBART is a forthcoming model that is said to have accessed DarkBERT training data, or is a model that will be loosely based off the concept. So far, it is only talked about and has not been released in the wild.
About the author

With 25 years of industry experience, Daemon Behr is a seasoned expert, having served global financial institutions, large enterprises, and government bodies. As an educator at BCIT and UBC, speaker at various notable events, and author of multiple books on infrastructure design and security, Behr has widely shared his expertise. He maintains a dedicated website on these subjects, hosts the Canadian Cybersecurity Podcast, and founded the non-profit Canadian Cyber Auxiliary, providing pro bono security services to small businesses and the public sector. His career encapsulates significant contributions to the IT and Cybersecurity community.
Other recent articles of note.
Discover more from Designing Risk in IT Infrastructure
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.





